Simplified Operations
New Split Update: Upgrading Cisco ISE has never been easier. With the new Split Upgrade feature, customers now have complete control over the upgrade process from the UI, allowing them to upgrade specific ISE nodes in parallel, with multiple iterations, at their convenience without experiencing any downtime. Say goodbye to complex and time-consuming upgrades.
Control Application Restart: Minimize Downtime, Maximize Efficiency. Downtime during certification renewals can be disruptive. Cisco ISE 3.3 introduces Controlled Application Restart, which allows customers to plan the renewals of the ISE administrative certificate, eliminating the need to reboot the entire ISE deployment at once without control. Schedule updates during low network usage periods, ensuring a smoother security update process without impacting operations.
Navigation improvement: ISE admins use the ISE UI in order to perform their job. ISE 3.3 introduces a new and improved navigation, allowing ISE admin to faster perform their tasks, with fewer clicks and without hiding their screen while navigating throughout ISE pages. Each ISE admin can now save the pages he or she is using most frequently on ISE and reduce the time it takes them to access those pages.
IPv6 Support: in addition to the RADIUS, TACACS+, and ISE management over IPv6, customers can now enable additional services over IPv6: the ISE guest portal can now be accessed over IPv6 address and serve guests on the IPv6 network. profiling of IPv6-enabled endpoints and doing posture checks is also available for IPv6-enabled endpoints.
Enhanced Platform Security
TPM Chip: Strengthen Security with the TPM Chip Security is paramount. Cisco ISE 3.3 with SNS-3700 (or virtual machines supporting VTPM) introduces the TPM Chip, a dedicated and secure storage location for sensitive information. With true random number generation for key generation, the TPM Chip enhances the security of stored data, providing you with peace of mind.
ISE Cipher Control: By allowing ISE admins to disable unwanted and weak ciphers manually, ISE 3.3 helps customers to meet compliance and regulations without the need to wait for the next release or a patch.
TLS 1.3 for ISE admins: ISE admins can now connect to ISE UI over TLS 1.3. TLS 1.3 provides enhanced security and improved performance by reducing latency and eliminating outdated cryptographic algorithms, ensuring stronger encryption and more efficient communication between clients and servers.
Certificate-Based Authentication for API calls: ISE 3.3 supports Certificate-based authentication for API calls. Certificate-based authentication offers stronger security by eliminating the vulnerabilities associated with traditional username and password authentication methods. It provides robust protection against credential theft, unauthorized access, and phishing attacks, ensuring a higher level of trust and authentication for users accessing sensitive systems or resources.
Visibility and Compliance
AI/ML based Profiling: Effortlessly Identify Unknown Endpoints with AI/ML Profiling Unidentified endpoints on the network can be a challenge. Cisco ISE 3.3 employs AI/ML Profiling and multi-factor classification (MFC) to swiftly identify clusters of similar unknown endpoints. This cloud-based ML engine helps customers categorize these devices accurately, making it easier to determine their nature and apply appropriate policies.
Unlock Valuable Insights with Wi-Fi Edge Analytics
Our exclusive Wi-Fi Edge Analytics feature enables customers, who use the Cisco Catalyst 9800 wireless controllers, to exchange data between ISE 3.3 and the controller and get profiling information from Apple, Intel, and Samsung devices, enhancing endpoint profiling.
This information includes endpoint-specific attributes such as model, operating system version, and firmware.
Multi Factor Classification: ISE 3.3 introduces a new way to profile endpoints on the network. The profile is no longer a descriptive string of the endpoint. Instead of that ISE uses MFC – Multi Factor Classification which breaks the profile into 4 categories: Manufacturer, Device Type, Model and OS. This allows our customers to build more granular policies, based on the different MFCs.
Posture for ARM based Windows: for customers who move to computers based on ARM processor, ISE 3.3 can now perform posture checks in order to check compliance status before letting those endpoints access to the network.
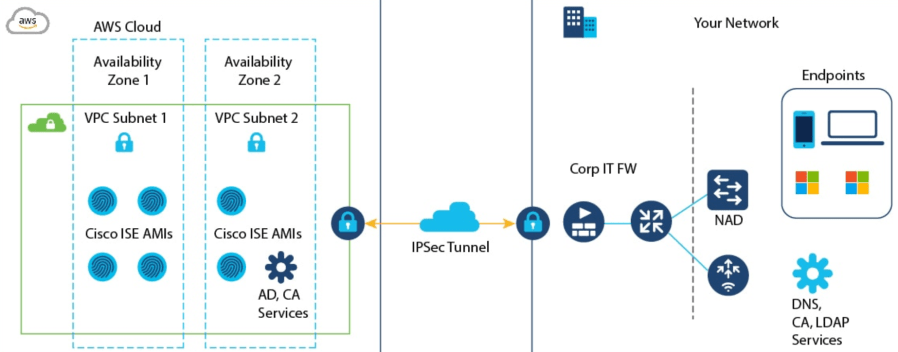
Cloud Availability
ISE 3.3 is going to be available on all the supported platforms: AWS, Azure, and Oracle Cloud. Release dates depend on the different cloud vendors:
ISE 3.3 on Azure – Already available
ISE 3.3 on OCI – Already Available
ISE 3.3 on AWS – Already Available
ISE 3.3 Resources: