Have you ever wondered how machines can understand customer preferences, house prices, or even text messages? The answer lies in feature engineering – one of the most crucial yet often overlooked aspects of machine learning.
What is Feature Engineering?
Feature engineering 💡 transforms raw data into meaningful features that help machine learning models better understand patterns and make more accurate predictions. Think of it like translating raw ingredients into a form ready for cooking. Just as a chef needs properly prepared ingredients to make a delicious meal, a machine-learning model needs well-engineered features to make accurate predictions.
Why is Feature Engineering Important?
Even the most sophisticated machine learning algorithms can fail if fed poor-quality features. Here’s why feature engineering matters:
- Better Model Performance: Well-engineered features can capture important patterns in your data that might otherwise be hidden. For example, instead of using raw dates, creating features like “day of the week” or “is_weekend” might better predict shopping behavior.
- Domain Knowledge Integration: Feature engineering allows us to incorporate our understanding of the problem into the model. If we’re predicting house prices, we might create a feature that combines square footage and location, knowing that price per square foot varies by neighborhood.
Understanding Data Types
Before diving into feature engineering techniques, let’s understand the two main types of data we typically encounter:
Quantitative Data
This is numerical data that you can perform mathematical operations on. For example:
- Age (25, 30, 45)
- Temperature (98.6°F, 102.3°F)
- Sales amount ($100, $250, $500)
Qualitative Data
This represents categories or qualities that can’t be measured numerically. For example:
- Colors (Red, Blue, Green)
- Education level (High School, Bachelor’s, Master’s)
- Customer satisfaction (Very Satisfied, Satisfied, Dissatisfied)
Essential Encoding Techniques for Beginners
When working with qualitative data, we need to convert it into numbers for our machine-learning models. Here are two fundamental encoding techniques:
One-Hot Encoding💡
Imagine you have a “color” feature with values: Red, Blue, and Green. One-hot encoding creates separate columns for each unique value:
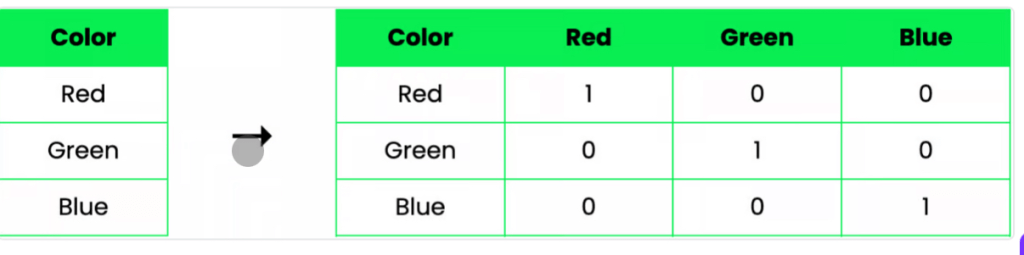
This is perfect for categorical data where there is no natural order between values. Each category is given equal importance, and the model can treat them independently.
Ordinal Encoding💡
When your categories have a natural order (like education levels), ordinal encoding assigns numbers based on that order:
Education Level Encoded Value
High School 1
Bachelor's 2
Master's 3
PhD 4This preserves the relative relationship between categories while converting them to a numerical format the model can understand.
Tips for Beginners
- Start Simple: Begin with basic feature engineering techniques and gradually explore more complex ones as you gain confidence.
- Understand Your Data: Before applying any encoding technique, understand what your data represents and how different features relate.
- Document Your Process: Track how you’ve engineered your features. This will help you replicate your success and troubleshoot issues.
- Validate Your Results: Always check if your feature engineering improves model performance. Sometimes simpler is better!
Remember, feature engineering is both an art and a science. It requires creativity, domain knowledge, and experimentation. As you practice, you’ll develop an intuition for which techniques work best in different situations.
Keep exploring and happy engineering!
Did you find this useful? I’m turning AI complexity into friendly chats & aha moments 💡- Join thousands in receiving valuable AI & ML content by subscribing to the weekly newsletter.
What do you get for subscribing?
- I will teach you about AI & ML practically
- You will gain valuable insight on how to adopt AI
- You will receive recommended readings and audio references for when you are on the go
Mike
Sources:



