Nexus: Replacing Supervisor 1 Modules with Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E Modules
- This migration process is disruptive for switches with one or two supervisor modules because the power must be turned off for the switch.
- Backward migration procedure (migrating from Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E modules to Supervisor 1 modules) is not provided.
- Recommend that you use Cisco NX-OS Release 5.2 (or later release) on the Supervisor 1 module while performing the migration.
- You cannot mix Supervisor 2 and Supervisor 2E modules in a production environment (this mix of modules is supported only while you are migrating from using Supervisor 2 modules to Supervisor 2E modules.
- If you plan to enable the admin VDC feature on the Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E modules, be sure to complete the entire migration procedure before enabling this feature (see the Cisco Nexus 7000 Series NX-OS Virtual Device Context Configuration Guide).
- The default-gateway command needs to be removed and replaced with ip route under the cmp-mgmt interface when SUP1 is upgraded to SUP-2/SUP-2E.
- If you are migrating Supervisor 1 Modules with Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E Modules, then replace ip default-gateway x.x.x.x’ with ip route 0/0 x.x.x.x in the config.
Step 1: Insert a USB drive in the top USB port (usb1) in the active supervisor 1 module. If the Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E module shipped with an extra USB drive, you can insert that USB drive in the usb1 drive on the Supervisor 1 module.
Step 2: Format the drive by using the format command.
switch(config)# format usb1:
Step 3: Copy all of the VDC configurations for the switch to the USB drive by using the copy running-config command. I recommend stepping into each vdc and performing your backup.
switch(config)# copy running-config usb1:configuration_file_name vdc-all
Step 4: Backup the installed licenses for the switch to the USB drive by using the copy licenses command.
switch(config)# copy licenses usb1:licenses_archive_file_name.tar
Step 5: Determine the Cisco NX-OS software release to use on the Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E modules.
Step 6: Copy the Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E version of the kickstart, system, and EPLD (optional) images to the USB drive.
Note: Use -s2- images with Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E modules. If you use an -s1- image with a Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E module, the supervisor will not boot up.
Step 7: Turn off the power to the switch by turning the power switch on each power supply from ON to STBY (Standby). The Output LED turns off on each power supply and the Status LEDs turn off on all of the supervisor and I/O modules.
Step 8: For each Supervisor 1 module installed in the switch, remove the module and replace it with a Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E module.
Note: Be sure the two supervisors are the same type. Do not mix Supervisor 1 with Supervisor 2 modules. Both Supervisors need to have the same amount of DRAM.
Step 9: Power up the switch by turning the power switch on each of its power supplies from STBY (standby) to ON. The Output LED on each power supply turns on and eventually turns green when the power supply is sending power to the switch. The Status LED on each installed supervisor module also turns on when the module begins to turn on. The supervisor that becomes active has a green ACTIVE LED (the standby supervisor module has an amber ACTIVE LED).
Step 10: Remove the USB drive from the Supervisor 1 module (this drive has copies of the Supervisor 1 configuration, license, and software images) and insert it in the Slot0: USB port on the active Supervisor 2 or Supervisor 2E module (ACTIVE LED is green).
Step 11: Connect a console to the active supervisor module.
Step 12: If you are setting up the initial configuration for the supervisor module, the initial setup script will ask you if you want to enforce the secure password standard. Make your selection, enter your password, and then confirm the password by entering it again.
—- System Admin Account Setup —-
Do you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no) [y]:
Enter the password for “admin”:
Enter the password for “admin”:
Step 13: When you are asked to enable admin VDCs, enter no
Do you want to enable admin vdc (yes/no) [no]:no
Step 14: When you are asked to enter the basic configuration, enter no
Step 15: When asked to log in, enter the login and password that you specified in step 12.
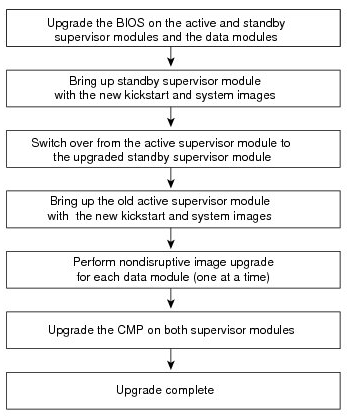
Step 16: Perform an upgrade to the appropriate nx-os version.
- Change the boot variable.
- Enter the copy running-config startup-config vdc-all command
- Enter the reload command to reload the switch.
boot kickstart bootflash:/n7000-s2-<kickstart image>.bin sup-1
boot system bootflash:/n7000-s2-<system image>.bin sup-1
boot kickstart bootflash:/n7000-s2-<kickstart image>.bin sup-2
boot system bootflash:/n7000-s2-<system image>.bin sup-2
Step 17: Copy the TAR archive containing the license files from the USB SLOT 0 drive to bootflash:, extract the archive, and install the licenses by using the copy, tar extract, and install license commands.
switch(config)# copy slot0:licenses_archive_file_name.tar bootflash:
switch(config)# tar extract bootflash:licenses_archive_file_name.tar to bootflash:
switch(config)# install license bootflash:license_file_name.lic
Step 18: Make sure that all I/O modules are online and that the standby supervisor is in ha-standby mode by using the show module command.
Step 19: If needed upgrade the EPLDs.
Note: To list the EPLDs running on your switch, use the show version module module_number epld command. If any of the versions that you list are older than what is recommended by Cisco, you should update the EPLDs.
Step 20: Restore the previously saved configurations by using the copy command to copy the configuration file in the USB drive to the running configuration.
Step 21: Save the configuration in the startup configuration by using the copy running-config startup-config vdc-all command.
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config vdc-all